COVID-19: TCTMD’s Dispatch for March Week 5
We’re curating a list of COVID-19 research and other useful content, and updating it regularly.

Since March 2020, TCTMD reporter Todd Neale has been writing up breaking news and peer-reviewed research related to COVID-19 every weekday. In July 2021, we transitioned to Mondays, Wednesdays, and Fridays. If you have something to share, tell us. All of our COVID-19 coverage can be found on our COVID-19 Hub.
***THE DISPATCH WILL RETURN AFTER ACC 2022***
March 31, 2022
More than half of Hong Kong’s population has now been infected with COVID-19, according to estimates by researchers at the University of Hong Kong, the New York Times reports. Contractors and medics from mainland China have “rushed to help” Hong Kong contain its outbreak, meeting mixed responses from the former British colony.
Compared with placebo, the antiparasitic drug ivermectin failed to prevent hospital admission or shorten the time spent in the emergency department in patients who were positive for COVID-19 and had experienced symptoms for less than a week. In the Brazilian trial, ivermectin was given for 3 days at a dose of 400 μg per kilogram per day. As reported in the New England Journal of Medicine, those assigned to ivermectin also had no improvement versus placebo in secondary outcomes, including viral clearance, length of hospitalization, or time to recovery. As reported by TCTMD’s Dispatch, the TOGETHER results were released earlier this month as an online “ground rounds.”
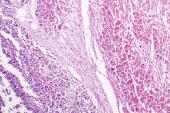
At 6-month follow-up, people under the age of 40 who were hospitalized for myocarditis after vaccination for COVID-19 had resolution of symptoms, with no major adverse cardiac events or subsequent hospitalizations, a small study shows. Speaking with Michael O’Riordan, one expert called the findings encouraging, noting that patients appeared to have no ongoing inflammation, with normalization of LVEF.
 This week, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said certain immunocompromised people and those over age 50 who received a COVID booster shot at least 4 months ago are now eligible for a second one. The following day, President Joe Biden received his second booster and urged Congress to provide additional funding to avoid shortages of vaccines, tests, and treatments. An Associated Press article quoted Biden as saying, “We have enough supply to give booster shots, but if Congress fails to act we won’t have the supplies we need this fall.”
This week, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said certain immunocompromised people and those over age 50 who received a COVID booster shot at least 4 months ago are now eligible for a second one. The following day, President Joe Biden received his second booster and urged Congress to provide additional funding to avoid shortages of vaccines, tests, and treatments. An Associated Press article quoted Biden as saying, “We have enough supply to give booster shots, but if Congress fails to act we won’t have the supplies we need this fall.”
Also this week, the Biden administration launched the website COVID.gov to help Americans find vaccines, testing, and oral medication providers in their community, as well as order free at-home test kits.
Adding pericardial effusion to the clinical and echocardiographic evaluation of COVID patients can improve prognostic evaluation, according to a prospective study. Of 530 patients hospitalized between March and September 2020, 75 had pericardial effusion, which was independently associated with a worse early warning score for mortality, Todd Neale reports.
 Despite having lower mean comorbidity burden than other racial groups, patients of American Indian and Alaska Native descent are more likely to die when hospitalized for COVID, a large US population-based study published in JAMA Network Open shows. “Although we do not discredit the role that comorbidities may play in COVID-19 outcomes, alternative contributing factors to disparate COVID-19 hospitalization and mortality outcomes among Indigenous populations must be considered,” the authors write.
Despite having lower mean comorbidity burden than other racial groups, patients of American Indian and Alaska Native descent are more likely to die when hospitalized for COVID, a large US population-based study published in JAMA Network Open shows. “Although we do not discredit the role that comorbidities may play in COVID-19 outcomes, alternative contributing factors to disparate COVID-19 hospitalization and mortality outcomes among Indigenous populations must be considered,” the authors write.
In a head-to-head article published in the BMJ, a global health policy consultant and the director general of the International Federation of Pharmaceutical Manufacturers and Associations argue for and against, respectively, the idea of COVID-19 vaccines and drugs being not-for-profit. While one side sees the pandemic as a chance for governments to share knowledge and waive intellectual property rules, the other side says the more serious problem is worldwide lack of equitable access to vaccination.
The European Medicines Agency this week said it has begun a rolling review of COVID-19 Vaccine HIPRA (HIPRA Human Health), a protein-based booster for adults who have been fully immunized with an mRNA and/or an adenovirus vaccine. The rolling review will continue until enough data are available for a formal marketing authorization application.
 Thirteen US states and the District of Columbia have had an uptick in COVID cases in the last 2 weeks, according to Health and Human Services (HHS) data collected by the New York Times. The increases range from a 6% rise in Maryland to 65% in New York.
Thirteen US states and the District of Columbia have had an uptick in COVID cases in the last 2 weeks, according to Health and Human Services (HHS) data collected by the New York Times. The increases range from a 6% rise in Maryland to 65% in New York.
The US Food and Drug Administration has added more states to its list of areas where sotrovimab (Xevudy, GlaxoSmithKline and Vir Biotechnology) is not authorized for treatment of mild-to-moderate COVID-19. The restrictions stem from evidence that the monoclonal antibody therapy is ineffective against the omicron B.A.2 variant.
In Lombardy, the most populated region of Italy, prisoners and prison staff were more likely to get testing and screening during the first COVID wave than those nonincarcerated, but during the second wave of the pandemic, cases in this group grew to more than 10 times that of the general population. In an article in JAMA Network Open, researchers argue that prison settings and populations are highly vulnerable to respiratory infections “and should be considered in response efforts during epidemic events.”
March 28, 2022
On Friday, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced that sotrovimab is no longer authorized to treat COVID-19 in certain regions with high rates of the Omicron BA.2 subvariant, due to evidence that the monoclonal antibody is unlikely to be effective against that strain. The treatment can no longer be used in the following states/territories: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Puerto Rico, Rhode Island, Vermont, and the Virgin Islands. STAT has more.
There’s a good chance the FDA will authorize a second booster dose—a fourth dose overall—for Americans older than 50, ABC News reports, citing officials familiar with the matter. The decision could come as soon as Tuesday, “though the fourth shots are likely to be only offered and not formally recommended,” according to the story.
 From the Associated Press: “China began its most extensive coronavirus lockdown in 2 years Monday to conduct mass testing and control a growing outbreak in Shanghai as questions are raised about the economic toll of the nation’s ‘zero-COVID’ strategy.” The city, with 26 million people, had managed previous, smaller outbreaks with more-limited lockdowns targeting areas where the virus was spreading.
From the Associated Press: “China began its most extensive coronavirus lockdown in 2 years Monday to conduct mass testing and control a growing outbreak in Shanghai as questions are raised about the economic toll of the nation’s ‘zero-COVID’ strategy.” The city, with 26 million people, had managed previous, smaller outbreaks with more-limited lockdowns targeting areas where the virus was spreading.
Patients infected with both influenza viruses and SARS-CoV-2 are more likely to require mechanical ventilation and have a greater likelihood of death compared with those infected with SARS-CoV-2 alone, according to a research letter in the Lancet. Coinfection with adenoviruses also was linked to an increase in mortality. “First, our results provide further support for vaccination against both SARS-CoV-2 and influenza viruses,” the authors write. “Second, they suggest that testing for influenza viruses is important in hospital inpatients with COVID-19 to identify patients at risk and a cohort of patients who might have different responses to immunomodulatory and antiviral therapy.”
Data set to be presented at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases next month indicate that the symptoms of long COVID may vary depending on the specific SARS-CoV-2 variant causing the initial infection. CIDRAP News has more.
 Case investigation and contacting-tracing (CICT) programs prevented at least 1.11 million COVID-19 cases and 27,231 hospitalizations over 60 days during the 2020-2021 winter peak of the pandemic in the US, according to estimates published in JAMA Network Open. “These findings suggest that CICT programs likely played a critical role in curtailing the pandemic,” the researchers say.
Case investigation and contacting-tracing (CICT) programs prevented at least 1.11 million COVID-19 cases and 27,231 hospitalizations over 60 days during the 2020-2021 winter peak of the pandemic in the US, according to estimates published in JAMA Network Open. “These findings suggest that CICT programs likely played a critical role in curtailing the pandemic,” the researchers say.
Another study investigating aspirin in the setting of COVID-19 has investigators saying that the cheap, ubiquitous drug may have a role to play in countries where expensive therapies are scant, even as the hints of benefit seen in observational studies fail to gain strong support in randomized trials. In this latest study, a large retrospective analysis published in JAMA Network Open, US adults with moderate COVID-19 who were given aspirin on the first day of hospitalization had a lower rate of 28-day in-hospital mortality compared with those who didn’t get aspirin (10.2% vs 11.8%). “Our study shows that aspirin can be used effectively in patients with moderate disease,” the lead author told TCTMD.
 The New York Times has put together an explainer on the antiviral pills designed to treat COVID-19: “Earlier this month, President Biden announced an initiative called ‘test to treat,’ which would allow people to visit hundreds of qualified pharmacy-based clinics, community health centers, and long-term care facilities across the country to get tested for the coronavirus and, if positive, receive antiviral medication on the spot.” The piece answers common questions about the pills and the initiative.
The New York Times has put together an explainer on the antiviral pills designed to treat COVID-19: “Earlier this month, President Biden announced an initiative called ‘test to treat,’ which would allow people to visit hundreds of qualified pharmacy-based clinics, community health centers, and long-term care facilities across the country to get tested for the coronavirus and, if positive, receive antiviral medication on the spot.” The piece answers common questions about the pills and the initiative.
A government fund created to reimburse clinicians for taking care of uninsured COVID-19 patients is no longer accepting claims for testing and treatment due to a lack of money, which means people who lack insurance coverage will no longer be able to get tested for free, according to the New York Times. “Uninsured people will now have to pay $125 to be tested at Quest Diagnostics, while other testing services may charge up to $195.”
Todd Neale is the Associate News Editor for TCTMD and a Senior Medical Journalist. He got his start in journalism at …
Read Full Bio




Comments